Adapter Design Pattern is used so that two unrelated or incompatible interfaces can work together. The main goal for this pattern is to convert an existing interface into another one the client expects.
There is always something incompatible between the old and the new. We create an adapter classes to manage such incompatibilities. To do this, we wrap an existing class with a new interface. Adapter Pattern is also known as Wrapper.

Advantages of Adapter Pattern
- Facilitates Integration: The Adapter pattern can facilitate the integration of different systems or components by providing a common interface that both can understand.
- Flexibility: You can swap or extend the adapters without affecting the rest of the system.
- Re-usability: Adapters can be reused with different adaptees, making it easy to use the same adapter with different systems.
- Improves Readability and Usability: The Adapter pattern allows the client code to remain separate from the adaptee code, which makes it easier to modify.
- Reduces Dependencies: The Adapter pattern can improve code maintainability by reducing the number of dependencies between components.
Disadvantages of Adapter Pattern
- Increases Complexity: The use of adapters can add additional layers of complexity to the codebase, which can make it harder to understand and maintain.
- Performance Overhead: Using an adapter can introduce performance overhead depending on the implementation, as additional processing may be required to translate data between different interfaces.
- Possible Tight Coupling: If the adapter is tightly coupled to the adaptee, it can create a dependency that may make it harder to modify the adaptee.
- May Obscure Errors: If errors occur within the adaptee code, they may be obscured by the adapter, which can make it harder to diagnose and fix problems.
When to use the Adapter Pattern?
- Legacy Code Integration
- Third Party Library Integration
- GUI Development
- Accessing Different Databases such as SQL, NoSQL or files
- Translate Requests and Responses between XML and JSON or SOAP and REST
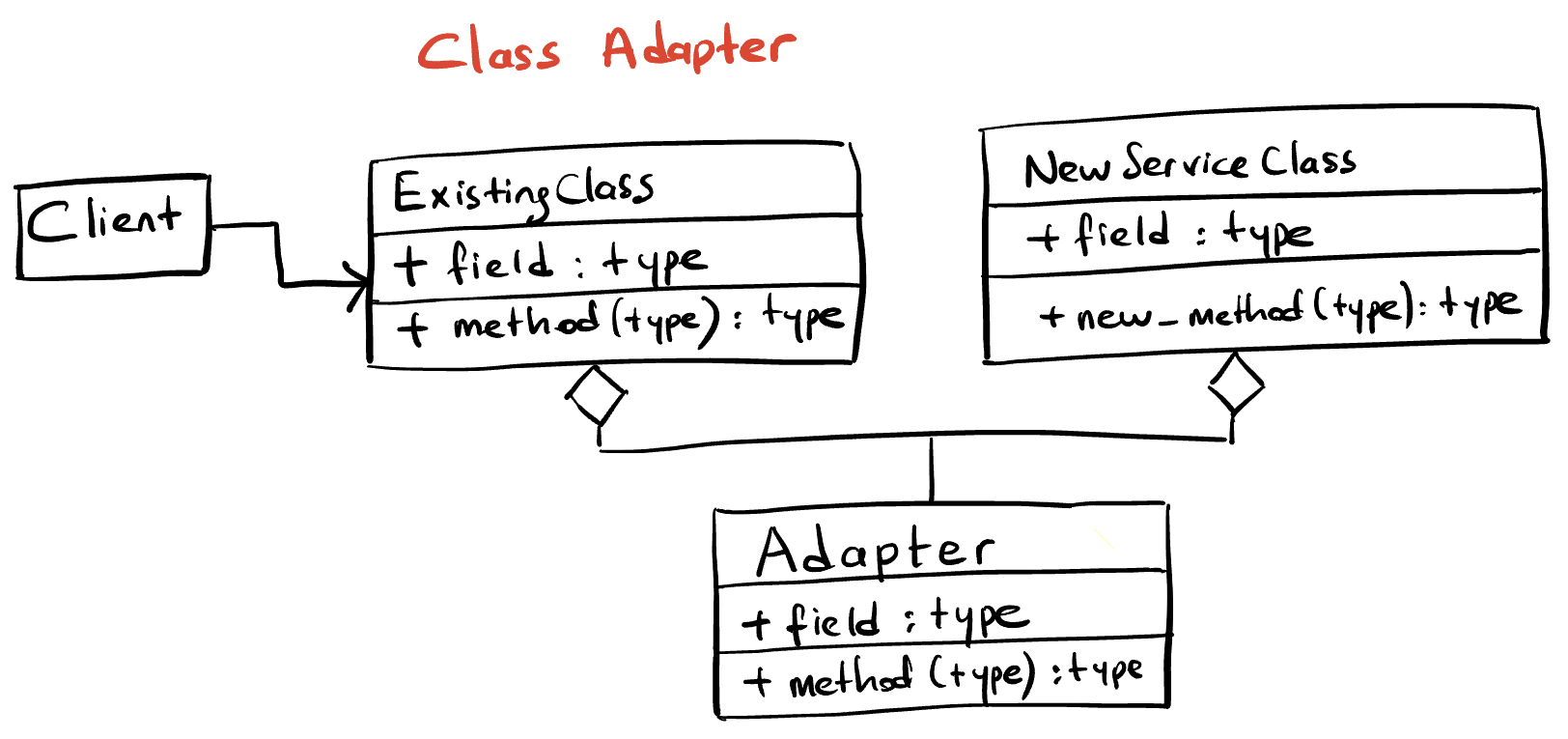
How to implement the Adapter Pattern? There are two ways to implement the adapter pattern: class adapter and object adapter.
- Class Adapter: The class adapter uses inheritance to extqend the existing class and implement the desired interface. It is simpler and faster.
![]()
- Object Adapter: The object adapter uses composition to wrap the existing class and delegate the interface methods to it. It is more flexible and robust, but it requires more code and may introduce some overhead.
![]()
Both approaches have their pros and cons, and you should choose the most suitable implementation, such as class adapter or object adapter.
In this part, I would like to show you an example of the adapter pattern that we used in a project. It needs to communicate to different bank account statement web services. Although the return response is the same, the request body information may differ for each bank. We have used an adapter pattern to convert the request to a specific request. According to the bank type, we have done the conversion of the request with the adaptee method. So we have provided an abstraction based on the bank type, and we can now implement numerous banks in our system. As a result, we have created a structure where we accept different requests and return the same response.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RequestMapping("/api/account-statements")
public class AccountStatementController {
private final AccountStatementFacade accountStatementFacade;
@GetMapping
ResponseEntity<AccountStatementResponse> getAccountStatements(@RequestHeader String bankType, @RequestBody String payload) {
return ResponseEntity.ok(accountStatementFacade.getAccountStatements(BankType.valueOf(bankType), payload));
}
}
1
2
3
4
public enum BankType {
A_BANK,
B_BANK
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
@Slf4j
public class AccountStatementClientFactory implements Factory<AccountStatementClient> {
private final BankType bankType;
public AccountStatementClientFactory(BankType bankType) {
this.bankType = bankType;
}
@Override
public AccountStatementClient build() {
switch (bankType) {
case A_BANK -> {
var username = "a_bank_user";
var password = "YV9iYW5rcGQ=";
var webServiceUrl = "soap-service@a_bank.com";
return new ABankAccountStatementClient(webServiceUrl, username, password);
}
case B_BANK -> {
var authURL = "auth@b_bank.com";
var webServiceUrl = "rest-service@b_bank.com";
var clientId = "b_bank_user";
var clientSecret = "Tl6zBL0xaPF=";
return new BBankAccountStatementClient(webServiceUrl, authURL, clientId, clientSecret);
}
default -> throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected bankType: " + bankType);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
public interface AccountStatementFacade {
AccountStatementResponse getAccountStatements(BankType bankType, String payload);
}
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Component
public class AccountStatementFacadeImpl implements AccountStatementFacade {
private final AccountStatementService accountStatementService;
@Override
public AccountStatementResponse getAccountStatements(BankType bankType, String payload) {
var accountStatements = accountStatementService.getAccountStatements(
new AccountStatementClientFactory(bankType).build(),
new AccountStatementRequestAdapter(bankType, payload).adaptee());
log.info("Request has been sent and response has been received from the [{}] external system. {}", bankType, accountStatements);
var accountStatementResponseConverterFactory = new AccountStatementResponseConverterFactory(bankType);
var accountStatementResponse = accountStatementResponseConverterFactory.build().convert(accountStatements);
log.info("Response received from the external system has been converted to the AccountStatementResponse object.");
return accountStatementResponse;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public interface Adapter<T> {
T adaptee();
}
@Slf4j
public class AccountStatementRequestAdapter implements Adapter<Object> {
private final BankType bankType;
private final String payload;
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
public AccountStatementRequestAdapter(BankType bankType, String payload) {
this.bankType = bankType;
this.payload = payload;
}
// Request is converted to a specific request in adaptee method.
public Object adaptee() {
try {
return switch (bankType) {
case A_BANK -> objectMapper.readValue(payload, ABankAccountStatementRequest.class);
case B_BANK -> objectMapper.readValue(payload, BBankAccountStatementRequest.class);
};
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
var message = String.format("An error occurred while trying to build the [%s] request.", bankType);
log.error(message);
throw new RuntimeJsonMappingException(message);
}
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public interface Factory<T> {
T build();
}
public class AccountStatementResponseConverterFactory implements Factory<Converter<Object, AccountStatementResponse>> {
private final BankType bankType;
public AccountStatementResponseConverterFactory(BankType bankType) {
this.bankType = bankType;
}
@Override
public Converter<Object, AccountStatementResponse> build() {
return switch (bankType) {
case A_BANK -> new ABankAccountStatementResponseConverter();
case B_BANK -> new BBankAccountStatementResponseConverter();
};
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public interface AccountStatementService {
Object getAccountStatements(AccountStatementClient accountStatementClient, Object accountStatementRequest);
}
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class AccountStatementServiceImpl implements AccountStatementService {
@Override
public Object getAccountStatements(AccountStatementClient accountStatementClient, Object accountStatementRequest) {
return accountStatementClient.getAccountStatements(accountStatementRequest);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
@Builder
public record ABankAccountStatementRequest(String accountId,
String startDate,
String endDate) {
}
@Builder
public record BBankAccountStatementRequest(String accountId,
String startDate,
String endDate,
String currency) {
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
public interface AccountStatementClient {
Object getAccountStatements(Object accountStatementRequest);
}
public class ABankAccountStatementClient implements AccountStatementClient {
private final String webServiceURL;
private final String username;
private final String password;
public ABankAccountStatementClient(String webServiceURL, String username, String password) {
this.webServiceURL = webServiceURL;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public Object getAccountStatements(Object accountStatementRequest) {
ABankAccountStatementRequest aBankAccountStatementRequest = (ABankAccountStatementRequest) accountStatementRequest;
return String.format("""
[A Bank] web service has been invoked with these parameters
webServiceURL: [%s]
username: [%s]
password: [%s]
requestPayload: [%s]
""", webServiceURL, username, password, aBankAccountStatementRequest);
}
}
public class BBankAccountStatementClient implements AccountStatementClient {
private final String webServiceURL;
private final String authURL;
private final String clientId;
private final String clientSecret;
public BBankAccountStatementClient(String webServiceURL, String authURL, String clientId, String clientSecret) {
this.webServiceURL = webServiceURL;
this.authURL = authURL;
this.clientId = clientId;
this.clientSecret = clientSecret;
}
@Override
public Object getAccountStatements(Object accountStatementRequest) {
BBankAccountStatementRequest bBankAccountStatementRequest = (BBankAccountStatementRequest) accountStatementRequest;
return String.format("""
[A Bank] web service has been invoked with these parameters
authURL: [%s]
webServiceURL: [%s]
clientId: [%s]
clientSecret: [%s]
requestPayload: [%s]
""", authURL, webServiceURL, clientId, clientSecret, bBankAccountStatementRequest);
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public interface Converter<I, O> {
O convert(I input);
}
public class ABankAccountStatementResponseConverter implements Converter<Object, AccountStatementResponse> {
@Override
public AccountStatementResponse convert(Object input) {
// Let's suppose the values are come from the input parameter.
return new AccountStatementResponse("1234", "A Bank",
"USD", "2022-04-30", "REF123",
"1000", "Credit", "Salary Payment",
"TRX123", "12:30 PM");
}
}
public class BBankAccountStatementResponseConverter implements Converter<Object, AccountStatementResponse> {
@Override
public AccountStatementResponse convert(Object input) {
// Let's suppose the values are come from the input parameter.
return new AccountStatementResponse("5678", "B Bank",
"EUR", "2023-04-30", "REF456",
"2000", "Debit", "Rent Payment",
"TRX456", "10:00 AM");
}
}
You can download the source code from the banking-integration.zip file.